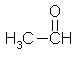
Acetaldehyde
| 원료 | ethylene; oxygen | ||||||||||||
| 생산물 | acetaldehyde | ||||||||||||
| 적용 | To produce acetaldehyde from ethylene by direct oxidation | ||||||||||||
| 설명 | Description: There are two variations of the process, one using oxygen and the other using air. The choice depends on local conditions such as oxygen cost, utility prices and ethylene purity. The process employs a catalyst solution of copper chloride containing small quantities of palladium chloride. The reactions are summarized as follows:
In the reaction, palladium chloride is reduced to elemental palladium and HCl and is re-oxidized by cupric chloride. During catalyst regeneration, the cuprous chloride is re-oxidized. The reaction and regeneration steps can be conducted separately or together. One-stage oxidation with oxygen: Ethylene and oxygen are fed into a vertical reactor (1) which is filled with catalyst solution. The reaction takes place under a slight pressure and at the boiling temperature of the aqueous solution. The reaction is exothermic by 242 kJ per mole acetaldehyde produced. This heat is removed by water evaporation, and the concentration of the catalyst solution is kept constant by means of a corresponding water supply. Acetaldehyde produced is condensed and scrubbed (2) with water from unreacted gas, which is recycled. Raw materials and utilities (per 1,000 kg acetaldehyde, 95% yield):
|
||||||||||||
| Properties in KDB |
Component Names and Formula
Click here to find more informations from KDB.
|