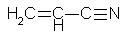Acrylonitrile
| 원료 | |||||||||||||
| 생산물 | Acrylonitrile | ||||||||||||
| 적용 | A process for the manufacture of acrylonitrile from propylene, anhydrous fertilizer-grade ammonia and air. 99 + % purity HCN and acetonitrile may be recovered as salable byproducts if desired. | ||||||||||||
| 설명 | Description: The above feeds are introduced into a fluid bed catalytic reactor operating at 5-30 psig and 750°-950℉. The reactor effluent is scrubbed in a countercurrent absorber, and the organic materials are recovered from the absorber water by distillation. Hydrogen cyanide, water, light ends and high-boiling impurities are removed from the crude acrylonitrile by fractionation to produce specification acrylonitrile product. A feature of the process is the high conversion obtained on a once-through basis in the fluid in the fluid bed reactor. Troublesome separation and recycling of unreacted raw materials is unnecessary. Catalyst: The fluid bed catalyst currently recommended in the process is Catalyst-49. This represents the fourth major level of catalyst improvement since the process was first commercialized. It produces more acrylonitrile per pound of propylene than its predecessors and because of this efficiency also reduce waste stream volumes. Operating conditions: The reactor operating conditions are defined above. Most of the fractionation is accomplished at atmospheric pressure. Yields: In addition to acrylonitrile some byproduct HCN is recovered. If desired, ammonium sulfate and acetonitrile also can be recovered as byproducts.
Commercial installations: More than 45 plants throughout the world with an aggregate capacity exceeding 6 billion pounds per year of acrylonitrile. Plant capacities range from about 20 million pounds to about 400 million pounds per year of acrylonitrile. |
||||||||||||
| Properties in KDB |
Component Names and Formula
Click here to find more informations from KDB.
|